Table of Contents
- 1. The Rise and Importance of Micro-Entrepreneurship
- 2. Low-Capital Digital Business Models
- 3. Essential Skills for Success
- 4. First Steps: From Idea to Action
- 5. The Micro-Entrepreneur’s Technology Toolkit
- 6. Growth Strategies: From Micro to Macro
- 7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 8. Responsible Management of Digital Assets
The traditional understanding of starting a business often required high capital, physical locations, and complex operational processes. However, the transformation brought by digitalization has largely eliminated these barriers. Today, entrepreneurship is more accessible than ever for anyone with an idea, a talent, or expertise. Micro-entrepreneurship lies at the heart of this new ecosystem, offering individuals the opportunity to start their own businesses with minimal risk and low capital.
This article will explore the opportunities offered by micro-entrepreneurship in the digital age and the practical steps for those who want to embark on this path. We will examine in detail the roadmap required to bring a micro-venture to life, from low-capital business models and essential skills for success to the technology toolkit and growth strategies. The goal is to show that it is possible to build a valuable business without large budgets.
1. The Rise and Importance of Micro-Entrepreneurship
Micro-entrepreneurship defines agile business models with low startup costs, usually managed by a single person or a very small team. The rise of this model is directly linked to technological advancements, the spread of remote work culture, and individuals’ search for financial independence. A large office or dozens of employees are no longer needed to reach global markets.Micro-ventures add flexibility and innovation to the economy. They offer fast and effective solutions to specific customer needs by focusing on niche markets that large companies cannot fill. This approach allows the entrepreneur to turn their passions and areas of expertise into a revenue model while also providing more control over their work-life balance.
2. Low-Capital Digital Business Models
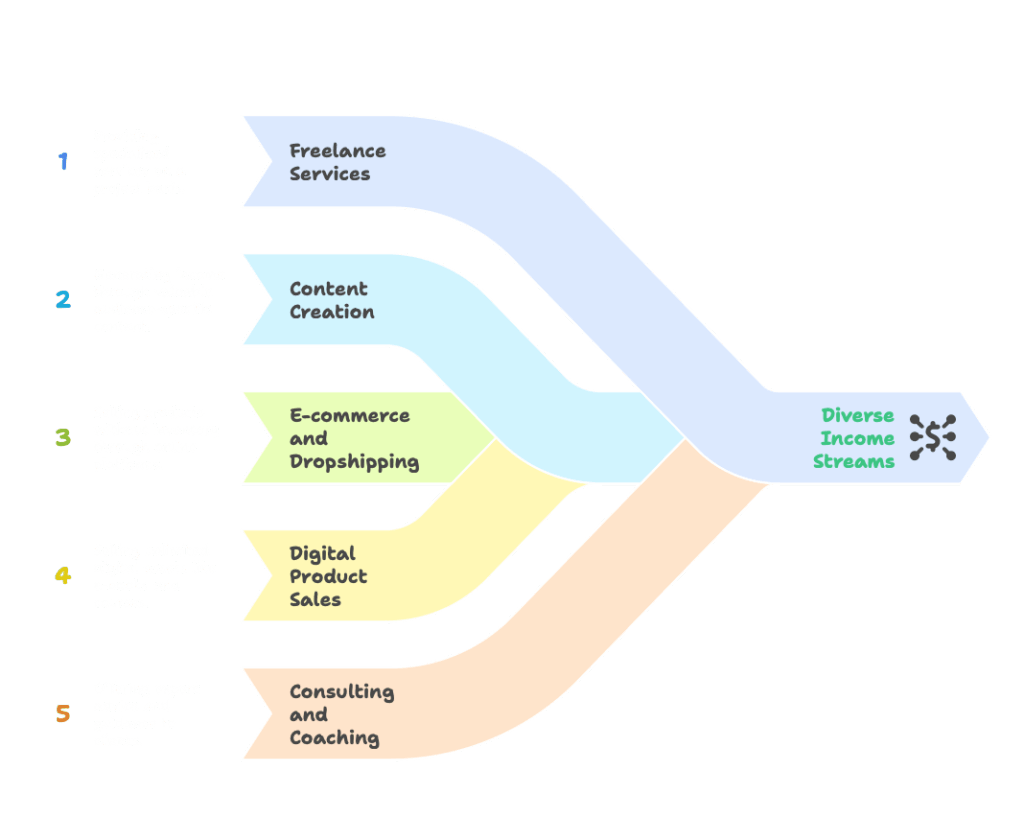
The digital world offers numerous business models based more on talent and knowledge than on capital. Here are some of the most popular ones:
- Freelance Services: Offering specialized services like software development, graphic design, copywriting, digital marketing, or virtual assistance on a project basis.
- Content Creation: Producing valuable content for a specific audience through a blog, YouTube channel, or podcast and generating income through advertising, sponsorships, or paid subscription models.
- E-commerce and Dropshipping: Selling physical products without holding inventory by shipping them directly from the supplier to the customer, or selling handmade, niche products on online platforms.
- Digital Product Sales: Creating digital assets that can be produced once and sold an unlimited number of times, such as e-books, online courses, design templates, software plugins, or stock photos.
- Consulting and Coaching: Offering in-depth knowledge and experience in a specific field (career, finance, health, etc.) to individual or corporate clients through sessions or programs.
3. Essential Skills for Success
Having just a good idea is not enough; the micro-entrepreneur needs to be versatile. The essential skills critical for success are:
- Digital Marketing: Mastering basics like SEO, social media management, email marketing, and content strategy to reach the target audience.
- Financial Literacy: Understanding pricing, budgeting, cash flow management, and basic tax obligations.
- Customer Relationship Management: Ensuring customer satisfaction, collecting feedback, and building a loyal customer base.
- Time Management and Self-Discipline: Being able to work efficiently and set priorities correctly without a distinct boss or office hours.
4. First Steps: From Idea to Action
Launching a micro-venture is possible through small, manageable actions rather than large, complex steps.
- Define Your Niche: Instead of trying to be “everything to everyone,” focus on a specific market segment you are passionate about and where you can solve a problem.
- Clarify Your Value Proposition: What is the unique value you offer your customers? What will convince them to choose you over your competitors?
- Develop a Minimum Viable Product/Service (MVP): Get real user feedback by launching your idea in its simplest, most functional form. Don’t delay the launch waiting for perfection.
- Create Your Digital Presence: Start with a simple website or a social media profile to create a platform where potential customers can find you.
5. The Micro-Entrepreneur’s Technology Toolkit
Low-cost or free technology tools can make even a one-person operation efficient.
- Project and Task Management: Trello, Asana, Notion
- Design and Visual Content: Canva, Figma
- Website and Landing Page: WordPress, Carrd, Webflow
- Payment Gateways: Stripe, Iyzico, PayTR
- Communication and Marketing Automation: Mailchimp, HubSpot
6. Growth Strategies: From Micro to Macro
Starting micro doesn’t mean staying micro. The next step after the business is established is to grow sustainably.
- Automate Processes: Dedicate more time to strategic tasks by automating repetitive jobs with automation tools.
- Outsource: Delegate tasks outside your area of expertise (accounting, virtual assistance, etc.) to freelancers.
- Diversify Revenue Streams: Instead of depending on a single service or product, add passive income models or complementary services.
- Form Strategic Partnerships: Develop joint projects with other micro-entrepreneurs who have the same target audience but are not competitors.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are some common pitfalls frequently encountered on the micro-entrepreneurship journey.
- Perfectionism: Constantly delaying the launch of the product or service to the market.
- Skipping Market Research: Acting on your own assumptions and ignoring real customer needs.
- Incorrect Pricing: Jeopardizing sustainability by setting prices below your value or losing customers with prices that are too high.
- Not Allocating Time for Marketing: Focusing only on product development and failing to announce it to anyone.
8. Responsible Management of Digital Assets
Building a digital business also brings ethical responsibilities. Customer trust is your most valuable asset.
- Data Privacy: Collect customer data transparently, store it securely, and fully comply with local laws (like GDPR).
- Transparent Communication: Always be open and honest about your services, pricing, and policies.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Both protect your own original work and respect the copyrights of others.
Micro-entrepreneurship is based not on the size of the capital, but on the power of the idea, the value of the talent, and the correctness of the strategy. Digital tools have removed barriers to market entry and enabled individuals to do business on a global scale. Success comes not from taking giant leaps, but from consistent and small steps taken in the right direction.
The issue is no longer about having enough money to start a business; it’s about having the passion to solve a specific problem and the courage to present this solution to the world. Individuals who manage this cycle correctly not only achieve financial freedom but also play an active role in shaping the digital economy.