Table of Contents
1. Digital Health Sector and Growth Potential
The digital health sector has shown remarkable growth in recent years. Telemedicine, mobile health applications, AI-powered diagnostic systems, wearable devices, and electronic health records form the core components of this field.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital health solutions. Patients and healthcare professionals became accustomed to services such as remote examination, online prescriptions, and digital health monitoring. This change exponentially increased the sector’s growth.
The global digital health market is expected to show annual growth of over 20 percent in the coming years. While this growth offers great opportunities for entrepreneurs, it also means high competition and strict regulations. Entrepreneurs who want to enter the sector need to understand these dynamics well.
2. Challenges Faced When Entering the Sector
The digital health sector has high barriers as well as high potential. Understanding these barriers is critical for a successful entry strategy.
The first challenge is the complexity of regulatory requirements. The healthcare sector is subject to strict regulations due to patient safety. A digital health product may fall into the medical device category, and in this case, approval processes can be long and costly.
The second challenge is integration problems with existing systems. Hospitals and clinics use different technology infrastructures. A new solution needs to work compatibly with these systems. This means technical complexity and high development costs.
The third challenge is data security and privacy. Health data is extremely sensitive. A data breach leads not only to legal problems but also to reputation loss. Investment in security infrastructure increases startup costs.
The fourth challenge is user acceptance. Healthcare professionals may be cautious about new technologies. Patients’ digital literacy levels vary. Education and support are needed for product adoption.
3. Regulation and Compliance
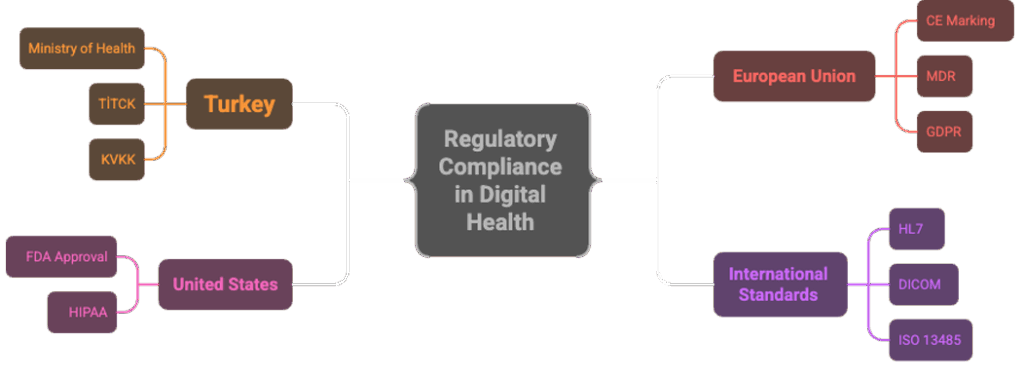
Regulatory compliance for digital health ventures is not optional but mandatory. Each market has its own specific regulations:
- In Turkey: The Ministry of Health and the Turkish Medicines and Medical Devices Agency (TİTCK) supervise digital health products. If products are classified as medical devices, CE marking and Ministry approval are required. Additionally, KVKK (Personal Data Protection Law) compliance is mandatory.
- In the European Union: CE marking is mandatory. MDR (Medical Device Regulation) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) compliance must be ensured. Clinical studies may be required depending on risk classification.
- In the United States: FDA approval is critical. Products are classified as Class I, II, or III according to risk level. HIPAA compliance is mandatory for protecting patient data.
- International Standards: Compliance with data standards such as HL7 and DICOM facilitates data sharing between systems. Quality management standards such as ISO 13485 are important for reliability.
4. Critical Factors for Success
To succeed in the digital health sector, it is necessary to focus on some strategic factors.
User-centered design is the most important factor. The product must solve the real needs of both healthcare professionals and patients. Simple and understandable designs should be preferred instead of complex interfaces. User testing should be an integral part of the product development process.
Creating clinical evidence builds trust. Clinical studies showing the product’s effectiveness provide credibility for both regulators and users. Collaborations with academic institutions are valuable in this process.
Strong data security infrastructure is essential. Encryption, access control, regular security testing, and data backup systems are necessary. Getting support from cybersecurity experts is a smart move.
Strategic partnerships accelerate growth. Collaborations with hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and pharmacy chains facilitate market access. These partnerships also provide valuable feedback during the product development process.
5. Successful Digital Health Venture Examples
Some digital health ventures have achieved remarkable success in this challenging sector.
Teladoc Health is one of the pioneers in the telemedicine field. Founded in 2002, the company delivered remote health consulting services to millions of people. User numbers multiplied during the pandemic, and the company became a major health technology platform.
Doctolib is one of Europe’s most successful digital health ventures. The platform, which started with online physician appointments in France, now serves 300 thousand healthcare professionals and more than 60 million patients. Full compliance with regulations and user-centered design were the keys to its success.
In Turkey, e-Nabız is a public sector digital health success. The system, which collects all health data on a single platform, is used by millions of citizens. This example shows what a scalable and secure health platform should be like.
6. Taking the First Steps
Starting a digital health venture requires a systematic approach.First, define the problem. What health problem are you solving? Does this problem really exist? Validate needs by interviewing target users. Identify gaps in the market by conducting competitive analysis.
Then develop a minimum viable product (MVP). Instead of trying to add all features at once, create a prototype that solves the core function. Test this with early users and improve based on feedback.
Determine your regulation strategy early. Is your product a medical device? What approvals do you need? Planning these processes from the start prevents you from encountering surprises later. Get consulting if necessary.
Make your financing plan. Digital health ventures are capital-intensive due to regulation and development costs. Prepare applications for angel investors, venture capital funds, or public support.
7. Conclusion: Shaping the Future in Digital Health
The digital health sector is both challenging and rewarding for entrepreneurs. Strict regulations, high technical requirements, and user expectations set high standards for success. However, with the right strategy and determination, these barriers can be overcome.
The key to success is prioritizing patient safety, fully complying with regulations, and offering solutions to real health problems. Technology is a tool; the real value lies in improving people’s quality of life.
Digital health is not just a business opportunity but also a social responsibility. When done right, it can facilitate millions of people’s access to healthcare services, reduce costs, and increase quality of life.
If you want to make a difference in healthcare, digital health entrepreneurship offers you this opportunity. Remember: Every great health innovation began with an entrepreneur’s bold step.